Unmyelinated Fibers Conduct Impulses Faster Than Myelinated Fibers
This leaping of action potentials from node to node is several times faster than the continuous propagation found in unmyelinated axons. Unmyelinated axons are thinner than myelinated axons.
Solved 6 Use The Following Information To Answer The Next Chegg Com
Propagation is faster in myelinated axons.
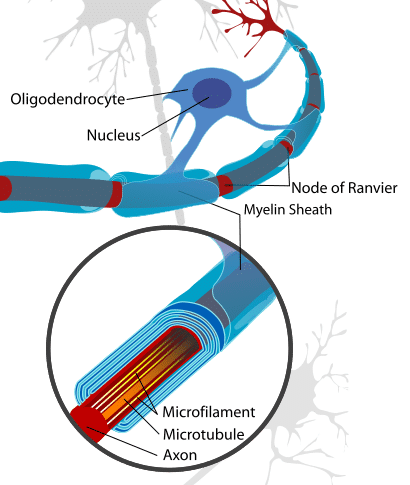
. There are no internodes in unmyelinated fibers. The key difference between myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibres is that the myelinated nerve fibres have myelin sheaths around them while the unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have the sheath. In unmyelinated fibers electrical impulses action potentials travel as continuous waves but in myelinated fibers they hop or propagate by saltatory conduction.
Loss of impulses is avoided in myelinated axons. Large unmyelinated fibers O 1 Conduct impulses at a slower velocity than myelinated nerves 2 Conduct impulses at a faster velocity than myelinated nerves 3 Conduct impulses at the same rate as small ones 4. Decreases reaction times to stimuli.
The latter is markedly faster than the former at least for axons over a certain diameter. Additionally the spaces between myelin sheaths nodes are highly concentrated with voltage gated sodium channels. Unmyelinated nerve fibers do not have myelin insulations and therefore the speed of the transmission of the nerve impulses is low.
The main purpose of myelin is to increase the speed at which electrical impulses propagate along the myelinated fiber. This occurs due to the large proportion of fatty substances that make up the myelin sheath. A neuron with unmyelinated axon has a comparatively lower speed of conduction of the nerve signals.
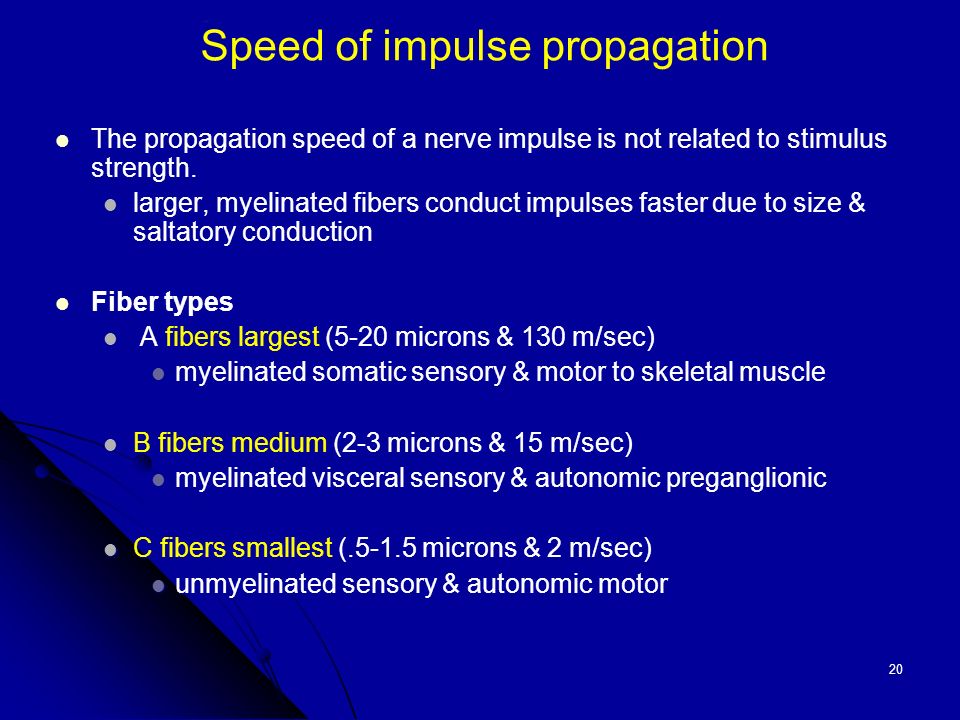
The conduction of nerve impulse is slower in unmyelinated axons. Difference Between Myelinated and Unmyelinated Nerve Fibres. The internode segments of myelinated axons allow local currents to travel quickly between nodes where the action potential is regenerated.
Which part of the neuron is responsible for generating a nerve impulse. In order to boost the speed at which electrical impulses travel through the myelinated fiber myelin serves the primary function of speeding up signal transmission. Myelinated neurons conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated neurons because nerve impulses jump over the myelin sheath rather than travel through it making the distance to the axon terminal shorter.
By acting as an electrical insulator myelin greatly speeds up action potential conduction Figure 314. Propagation is faster in myelinated axons. The axon of the neurons may be myelinated with myelin sheath or unmyelinated without myelin sheath.
Which part of the neuron is responsible for generating a nerve impulse. Active transport of sodium and potassium is faster in myelinated fibers. This is important because there is a disease whereupon the bodys own immune system attacks the myelin sheath around the axons in the central nervous system.
Related Posts Why Do Impulses Travel Faster In Myelinated Neurons. The conduction of nerve impulses is faster in myelinated axons. There is more chance of losing impulses.
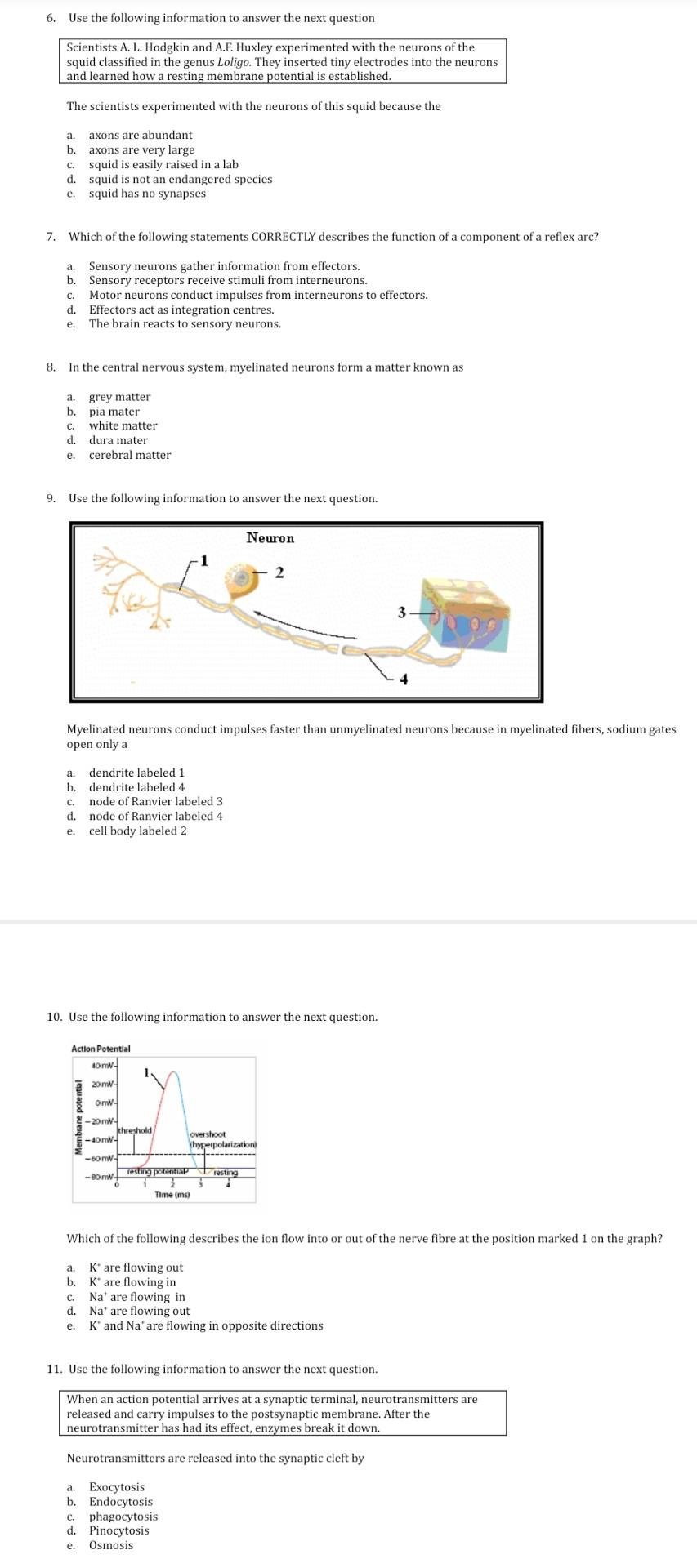
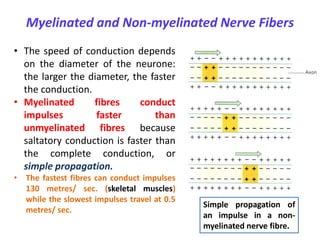
Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated fibers. Myelin speeds the conduction of nerve impulses by a factor of 10 compared to unmyelinated fibers of the same diameter. Why not all the axons mylinated.
The main difference between these two types of neurons is the speed of conduction of impulse. Additionally the spaces between myelin sheaths nodes are highly concentrated with voltage gated sodium channels. Myelinated axons transmit action potentials faster than unmyelinated axons.
A neuron with unmyelinated axon has a comparatively lower speed of conduction of the nerve signals. Furthermore the nerve impulse transmission is faster in. Conduction of an action potential is much faster along a myelinated fiber than along an unmyelinated one because the action potential can jump from node to node along the fiber.
Suggestions for the advantages include. Facilitated diffusion of sodium and potassium is faster in myelinated fibers. Electrical impulses action potentials travel as continuous waves in unmyelinated fibers but in myelinated fibers they hop or propagate through saltatory conduction which causes them to.
Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses faster than myelinated fibers. In unmyelinated fibers electrical impulses action potentials travel as continuous waves but in myelinated fibers they hop or propagate by saltatory conduction. Most neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system are myelinated because they require fast conduction speed such as neuron involved in spinal reflexes.
Myelinated axons are thicker than unmyelinated axons. Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses faster than myelinated fibers. Which of the following types of neurons carry impulses away from the central nervous system CNS.
Why are some neurons Unmyelinated. Diffusion of ions along the axoplasm is faster. Why are myelinated fibers faster than unmyelinated.
Myelinated neurons conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated neurons because nerve impulses jump over the myelin sheath rather than travel through it making the distance to the axon terminal shorter. For example whereas unmyelinated axon conduction velocities range from about 05 to 10 ms myelinated axons can conduct at velocities up to 150 ms. There are more internodes in unmyelinated fibers.
Different nerve fibers will conduct their impulses at different velocity depending on the size of the fiber and whether or not it is myelinated. July 26 2018 Posted by DrSamanthi. Promotes the ability to escape from sudden predatory attack.
Myelinated neurons conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated neurons because nerve impulses jump over the myelin sheath rather than travel through it making the distance to the axon terminal shorter. A neuron with myelinated axons can conduct the impulse at a faster speed since the myelin sheath acts as the insulator that helps to propagate the electrical signal faster. Compared to myelinated neurons unmyelinated neurons are slower in terms of conducting impulses and are found in the peripheral nervous system especially visceral nervous system and the gray matter of the nervous system.
Why Do Non Myelinated Nerve Fibres Even Exist As Myelinated Ones Can Actually Conduct Impulses Faster Quora

Action Potential Velocity Article Khan Academy

Cell Biology Why Is Saltatory Conduction In Myelinated Axons Faster Than Continuous Conduction In Unmyelinated Axons Biology Stack Exchange

02 Central Nervous Systemppt692 4

The Nervous System 2 Categories In Nervous System Central Nervous System Cns Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System Pns Nerves Outside Ppt Download

Action Potential L4 Ppt Video Online Download

Action Potential Velocity Article Khan Academy

Nervous System Overview Ppt Video Online Download

Myelinated And Unmyelinated Axons Structure Importance

1 Organsorgans Brain Spinal Cord Cns And Nerves Pns Functionfunction Integration Of All Parts Organs Tissues Cells Allows Control Of Parts Ppt Download
Human Physiology Neurons The Nervous System

Day 2 Pages Cell Membrane Potential A Cell Membrane Is Usually Polarized As A Result Of Unequal Ion Distribution Distribution Of Ions Ppt Download

The Nervous System Two Parts Central Peripheral Brain And Spinal Cord Ppt Download

Nervous System Some Activities That Require Activity From The Nervous System Feeling Thinking Remembering Moving Being Aware Of The World Around You Helps Ppt Download

Solved Different Nerve Fibers Will Conduct Their Impulses At Chegg Com
Myelin The Myelin Sheath Effects Of The Myelin Sheath Teachmephysiology

Comments
Post a Comment